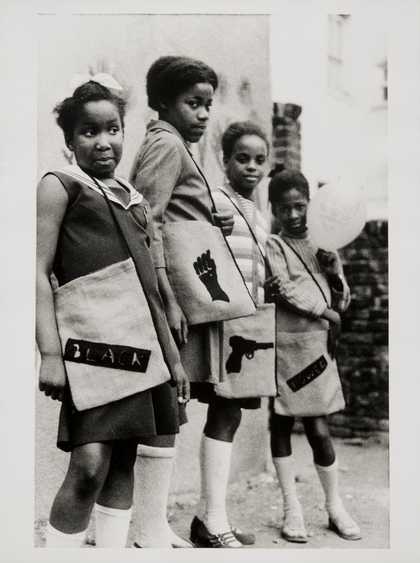

Neil Kenlock MBE, Black Panther school bags 1970, printed 2010. Tate. © reserved.
Ideas into Action 1965–1980
14 rooms in Modern and Contemporary British Art
Artists begin working with ideas and images that can be rapidly transmitted in an increasingly interconnected world, addressing political and social issues
The late 1960s is seen by many as a high point in cultural experimentation and revolutionary ideals. Artists begin developing art that is more concerned with ideas than aesthetics. They also want to democratise how art is produced, shared and experienced. These artists do not think of their work as something to be owned but instead as a way to exchange ideas. They emphasise process: how and why you make something is more important than what you produce. They often move out of their studios to work in the streets and don’t use traditional art materials. It seems to be an art of endless possibility, as artists embrace new materials, processes and actions.
As the 1960s becomes the 1970s, artists in Britain increasingly use these strategies to address social issues. These include: the personal and political injustices identified by the feminist movement, the poor condition of social housing, the legacy of British colonialism, experiences of racism, and escalating global political tension, including war in Vietnam.
Technological developments, exemplified by the 1969 moon landing of Apollo 11, also mark this era. Another of the most profound legacies of the time is the women’s liberation movement. Soon after the UK joins the European Communities in 1973, the global oil crisis contributes to economic recession and severe inflation. The country sees nationwide strikes by workers demanding that their pay keeps up with the rising cost of living. Many artists respond to this crisis that drives people to gather and protest.
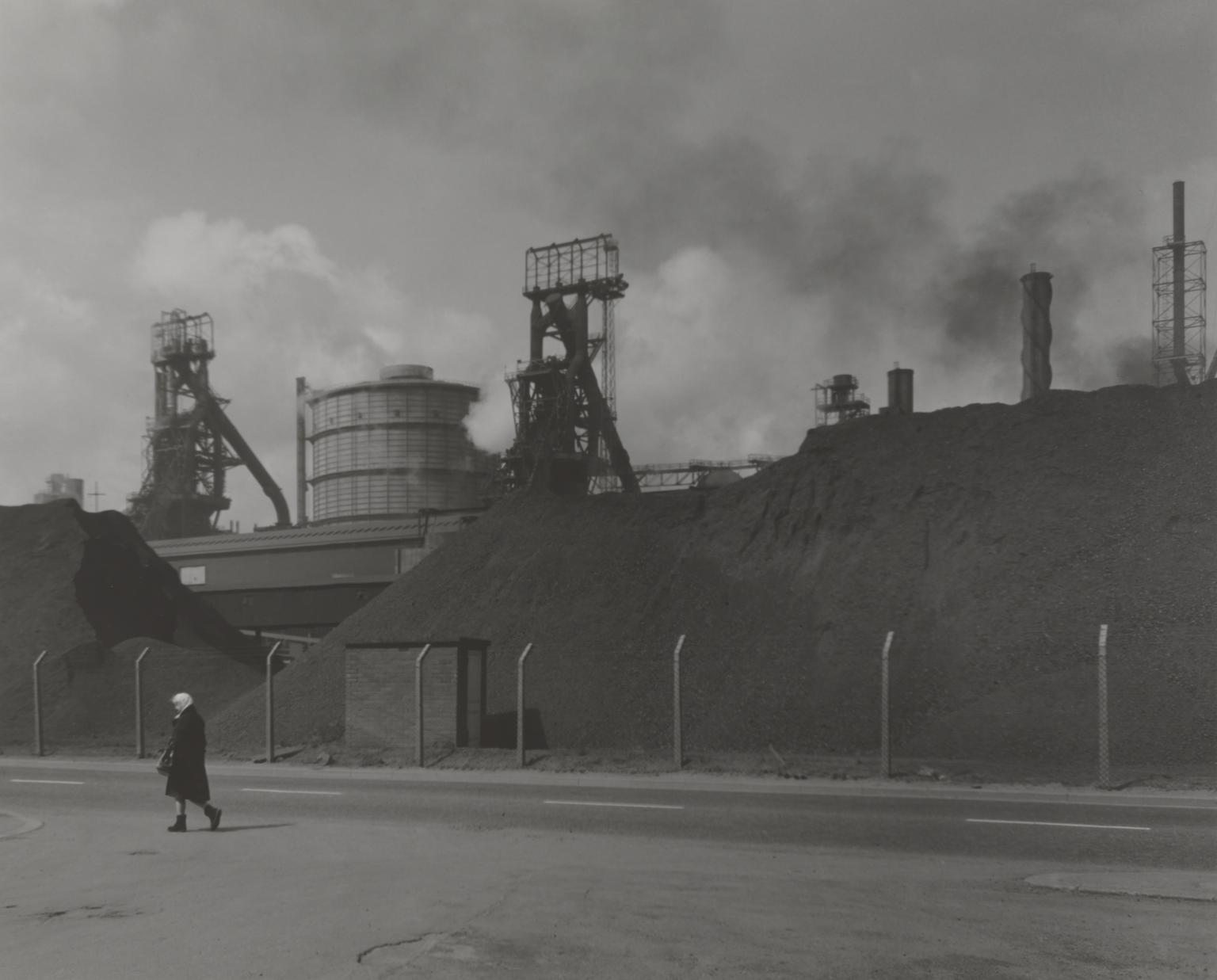

Chris Killip, Woman walking past blast furnaces, Grangetown, Teeside 1976, printed 2012–13
This group of images capture the changing landscapes of the northeast of England during a period of high unemployment and deindustrialisation. In these photographs, Chris Killip documents the windowless purpose-built homes that became typical across the northeast, the dying local shipbuilding industry, as well as community leaders such as a trade union official. Killip took these photographs after being made the Northern Arts Photography Fellow in Newcastle in 1975.
Gallery label, January 2025
1/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
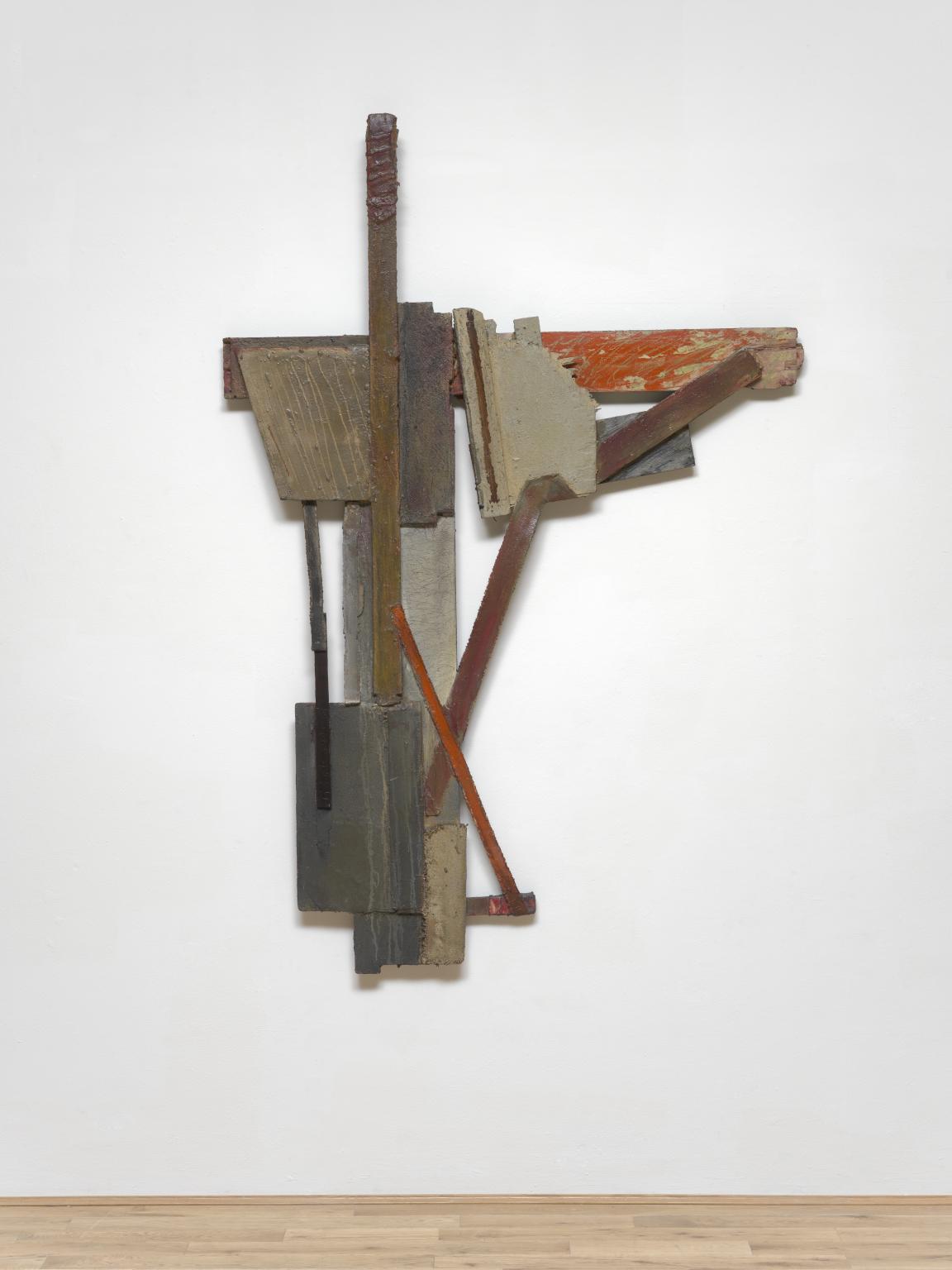

Janet Nathan, Zeloso 1979
Janet Nathan’s constructions are made from a range of found objects. She collected driftwood, resin and painted wood from skips or from the shoreline, most often along the River Thames. Coastlines were an important source of inspiration for the artist, both in terms of materials and subject matter. The work’s asymmetrical arrangement forms a cross shape, a recurring symbol in the artist’s practice. Although apparently abstract at first glance, the work could evoke the form of a dock, jetty or mudflat.
Gallery label, January 2025
2/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
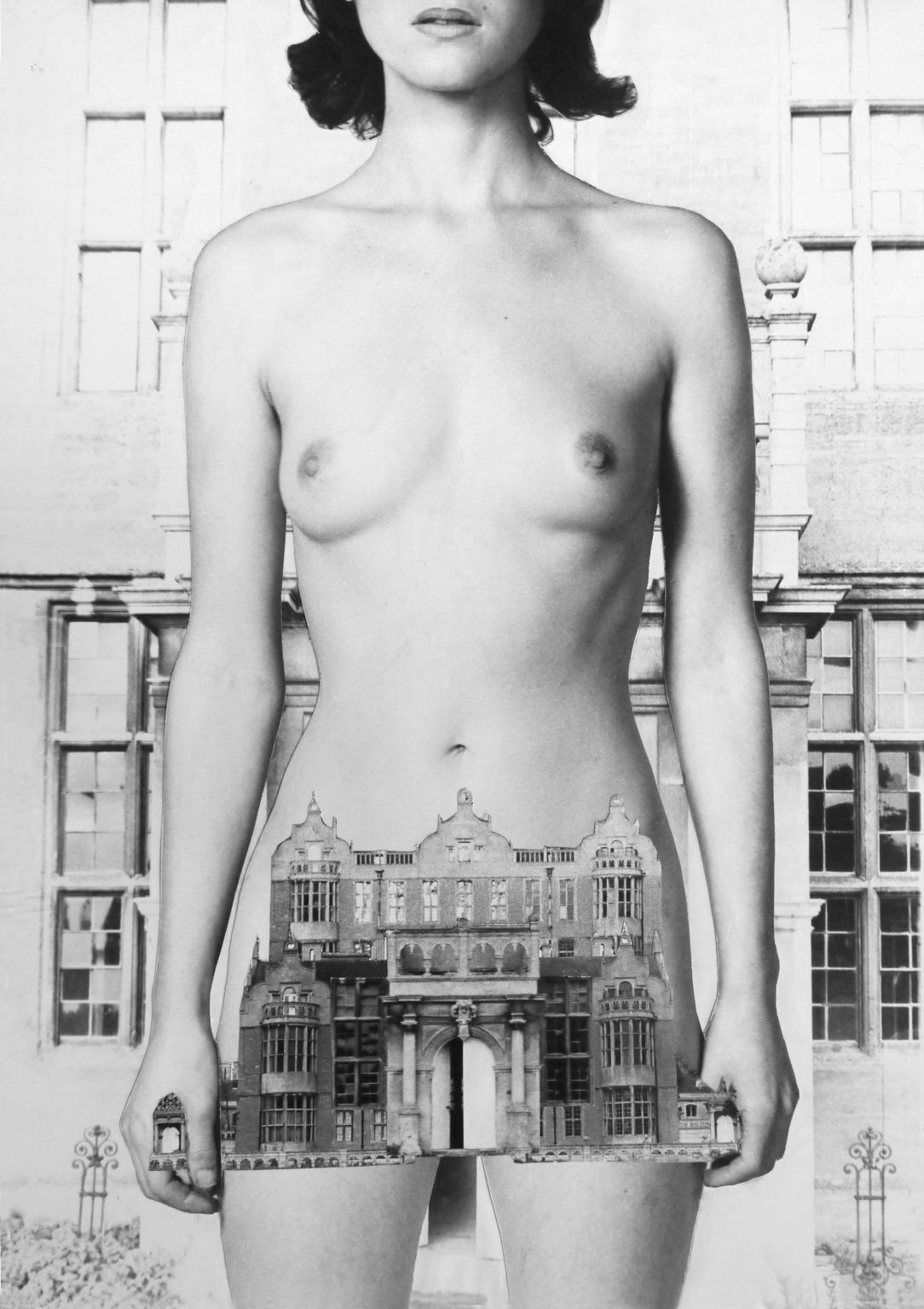

Penny Slinger, Perspective 1970–7
These photo-collages are part of a series of self-portraits Penny Slinger made in the near derelict Lilford Hall in Northamptonshire. Speaking of the photographs, Slinger found: ‘They had an evocative power, which compelled me to use them as the basis for a series of collages. I felt that this Stately Home had something yet to contribute to my own exploration of the psyche.’ During the seven-year process of making the series, Slinger found herself ‘emerging from a nightmare of others’ projections.’ Her photo-collages were published in 1977 as a book titled An Exorcism.
Gallery label, January 2025
3/27
artworks in Ideas into Action

Richard Long CBE, Turf Sculpture 1967
Long finished this work in Bristol in his second year on the Advanced Course. He cut the soil, removing the turf segments and configured its formal arrangement before making a photographic record. The cut turf was then relayed so that the segments would grow back into the earth.Critics have noted a connection between Long’s arrangement of the turf and the basic geometric shapes that characterised the formalist work of tutors such as Anthony Caro. Long has refuted this view by explaining the significance of the archetypal natural forms and the ephemerality of this intervention.
Gallery label, May 2007
4/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
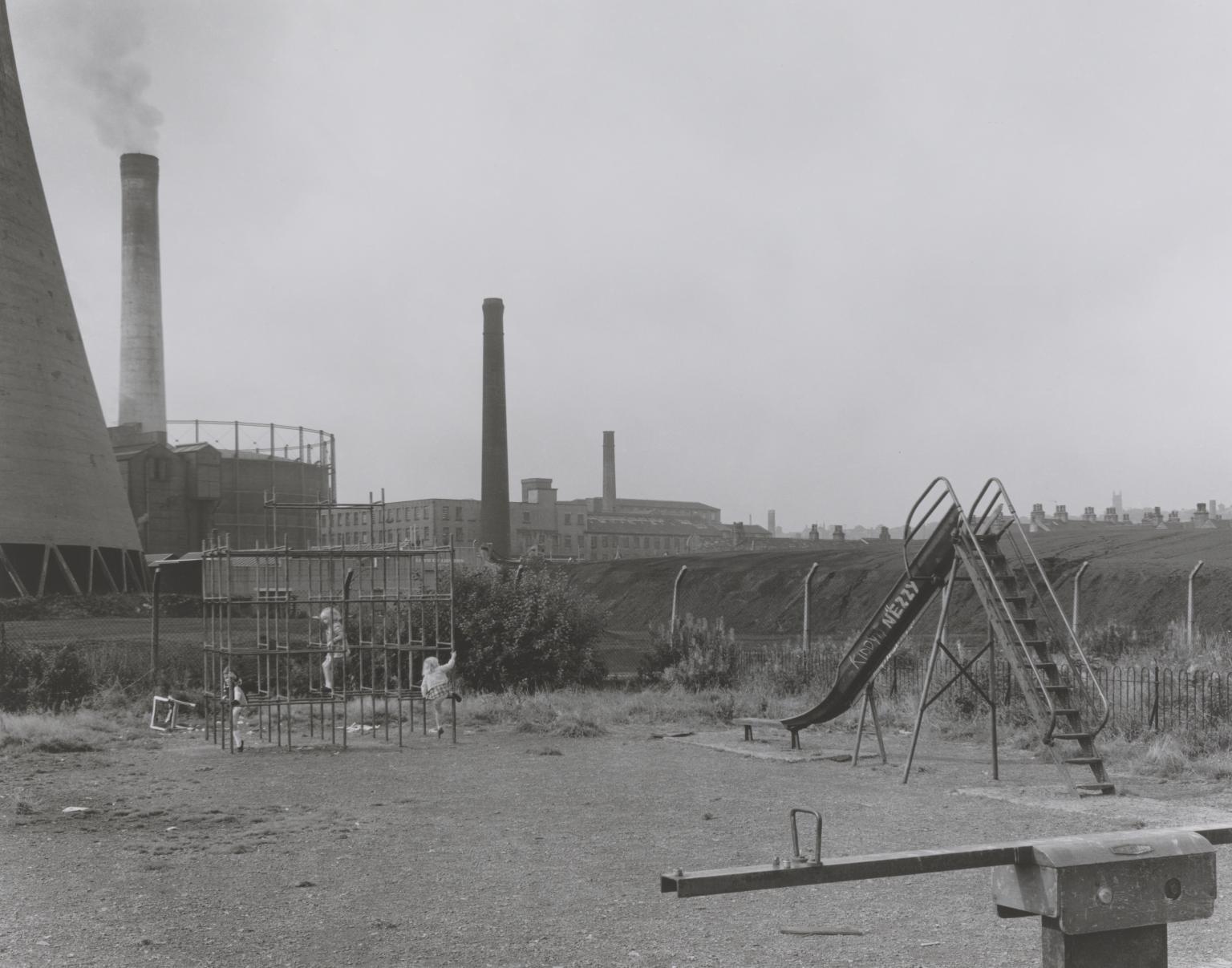

Chris Killip, Playground with three girls 1974, printed 2010
This one of six black and white photographs in Tate’s collection from the British photographer Chris Killip’s series Huddersfield, Yorkshire 1973–4 (see Tate P81015–P81020). They were taken after Killip received an Arts Council commission to photograph Huddersfield in Yorkshire and Bury St Edmunds in Suffolk for the exhibition TWO VIEWS – TWO CITIES, which was held at Huddersfield Art Gallery and Bury St Edmunds Art Gallery in 1973. The photographs of Huddersfield present dignified images of local inhabitants, such as Whippet Fancier 1973 (Tate P81015) and Brass Band Member 1973 (Tate P81018), and carefully observed and composed shots of derelict shops and tenement buildings, as in Jimmy’s T.V. Repair Shop 1974 (Tate P81016) and Windowless Terrace 1973 (Tate P81019). Killip’s working practice is distinctive for the way he immerses himself into the communities he photographs and builds relationships with his subjects over a long period of time. This close level of involvement shows itself in the Huddersfield series through images that are sensitive to the local environment and its inhabitants.
5/27
artworks in Ideas into Action

Gustav Metzger, Stockholm June: A project for Stockholm 1-15 June 1972, Phase 1 and Phase 2 1972, 2013
6/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
Sir Horace Ové CBE, Darcus Howe Speaks at the Mangrove Demonstration 1970, printed 2023
On 9 August 1970, a march took place to protest the police harassment of Black communities, including at The Mangrove, a Caribbean restaurant in Notting Hill, London. Nine protesters were charged with incitement to riot. In these photographs, Horace Ové captures significant moments from the march and subsequent trial. All nine activists were eventually acquitted, signalling the first judicial acknowledgment of racial hatred within the Metropolitan Police. These photographs come from a body of work Ové made between 1967 and 1970 documenting key events in the British civil rights movement.
Gallery label, August 2024
7/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
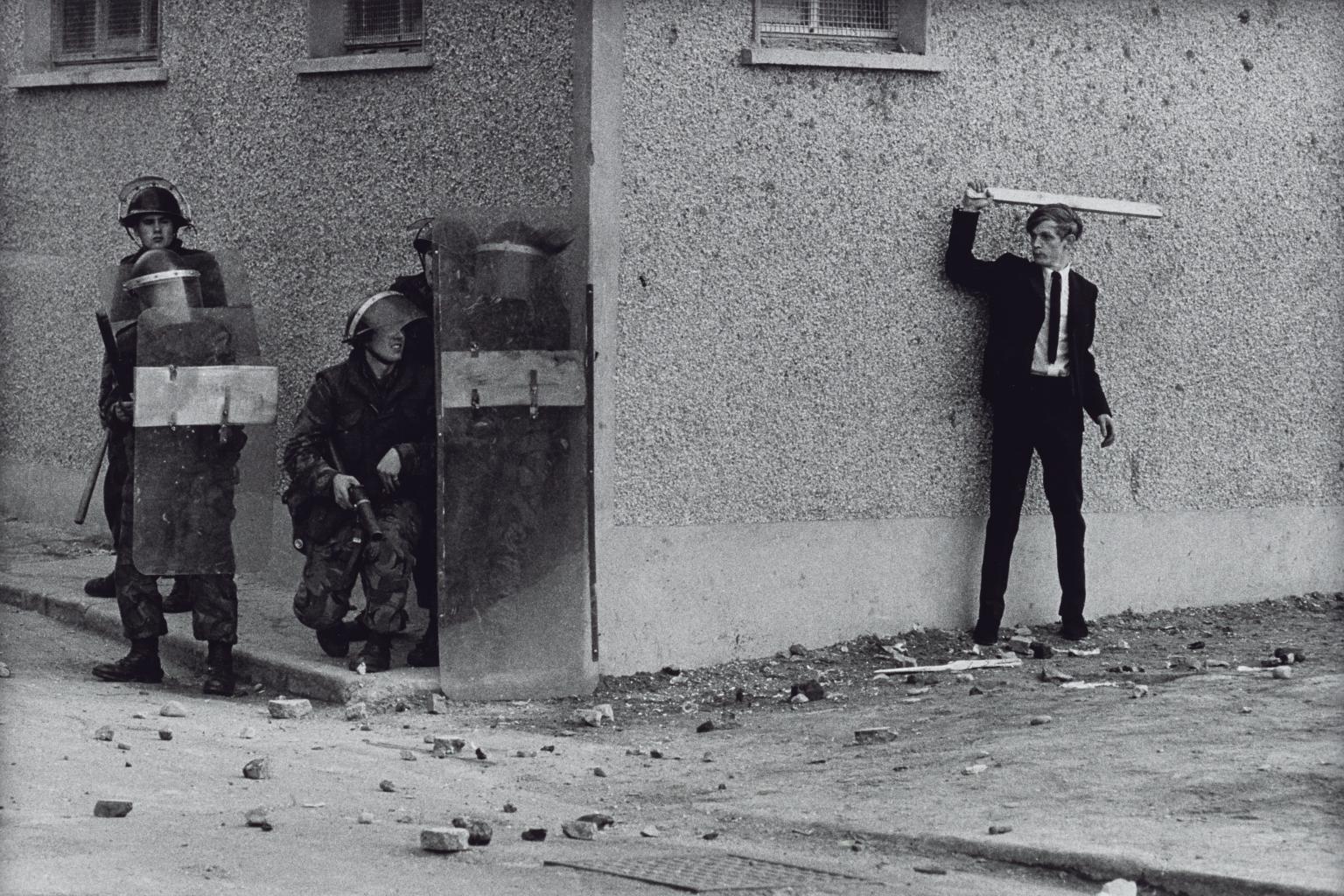

Sir Don McCullin CBE, Northern Ireland, The Bogside, Londonderry 1971, printed 2013
8/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
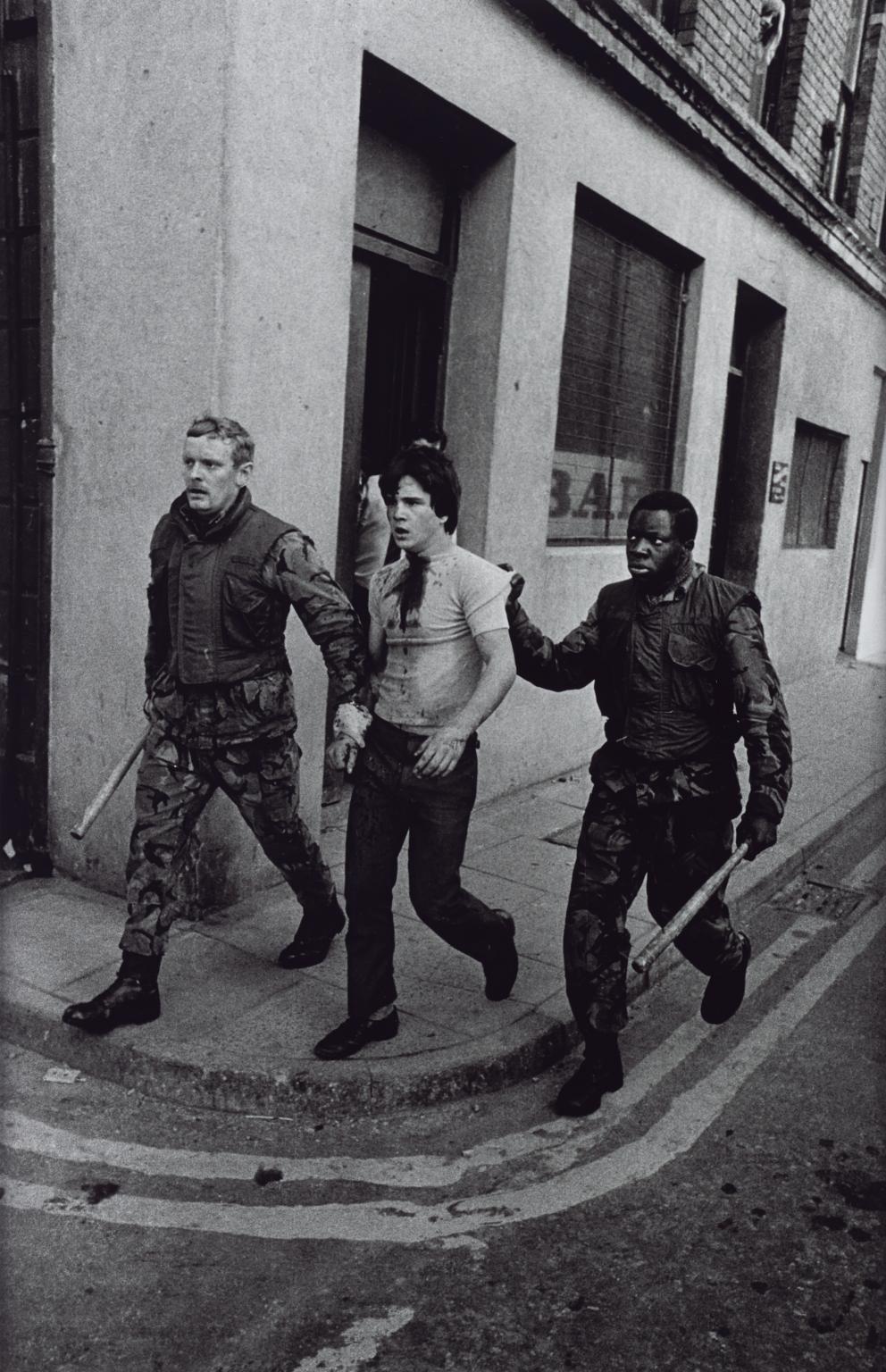

Sir Don McCullin CBE, British Soldiers in The Bogside, Londonderry, Arresting a Catholic Youth 1971, printed 2013
9/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
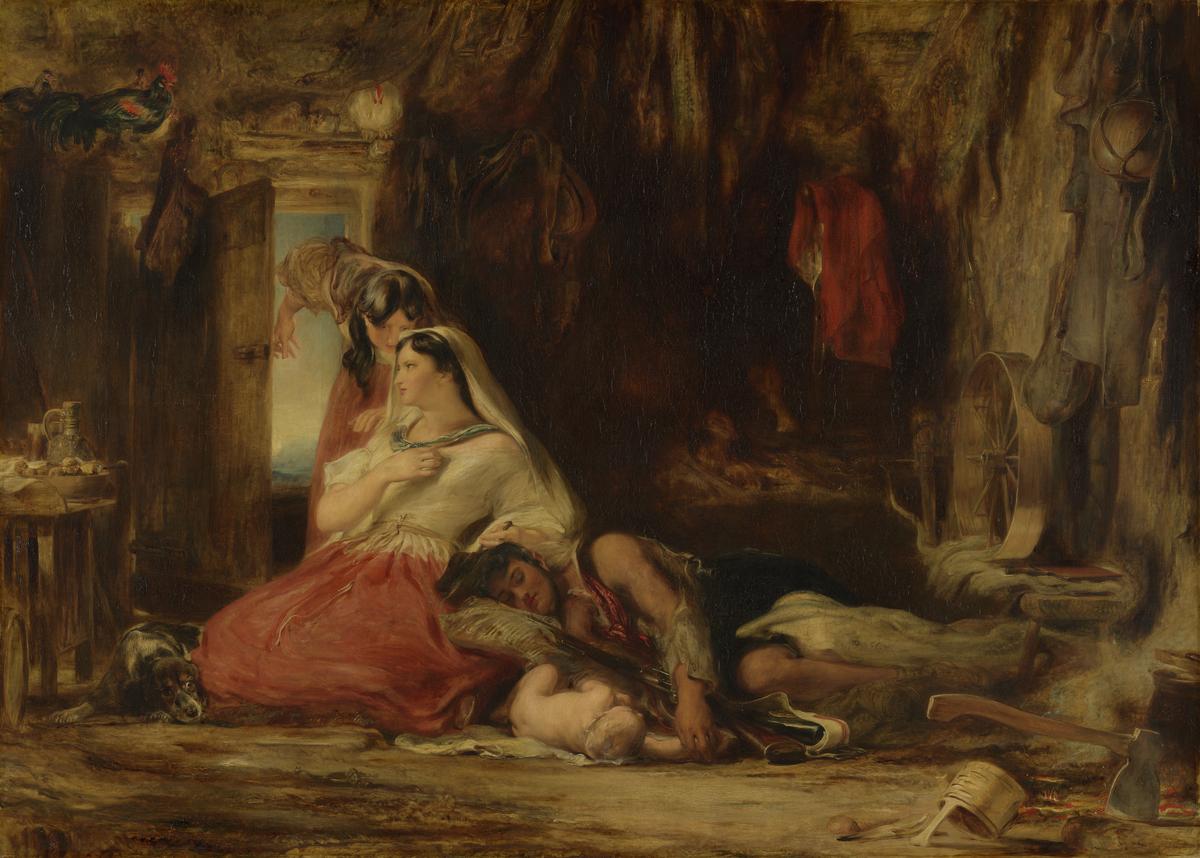

Sir David Wilkie, The Peep-o’-Day Boys’ Cabin, in the West of Ireland 1835–6, exhibited 1836
Some of Wilkie’s most popular pictures showed life and folk traditions in rural Scotland, familiar from his boyhood. Later, in 1835, he visited Ireland, which he compared to Spain for its picturesque potential. He exhibited this picture the following year. It evokes the ‘state of primeval simplicity’ he found in Galway and Connemara, while underplaying the political and religious unrest implied by the title.Peep-o’Day Boys were Protestant guerrillas. They raided Catholic rebels at dawn, during uprisings in the 1780s and 90s. Wilkie had first planned a more contentious subject: a Whiteboy, from another group who championed oppressed tenants.
Gallery label, May 2007
10/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
Sir Horace Ové CBE, The Mangrove Nine at Court House 1970, printed 2023
On 9 August 1970, a march took place to protest the police harassment of Black communities, including at The Mangrove, a Caribbean restaurant in Notting Hill, London. Nine protesters were charged with incitement to riot. In these photographs, Horace Ové captures significant moments from the march and subsequent trial. All nine activists were eventually acquitted, signalling the first judicial acknowledgment of racial hatred within the Metropolitan Police. These photographs come from a body of work Ové made between 1967 and 1970 documenting key events in the British civil rights movement.
Gallery label, August 2024
11/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
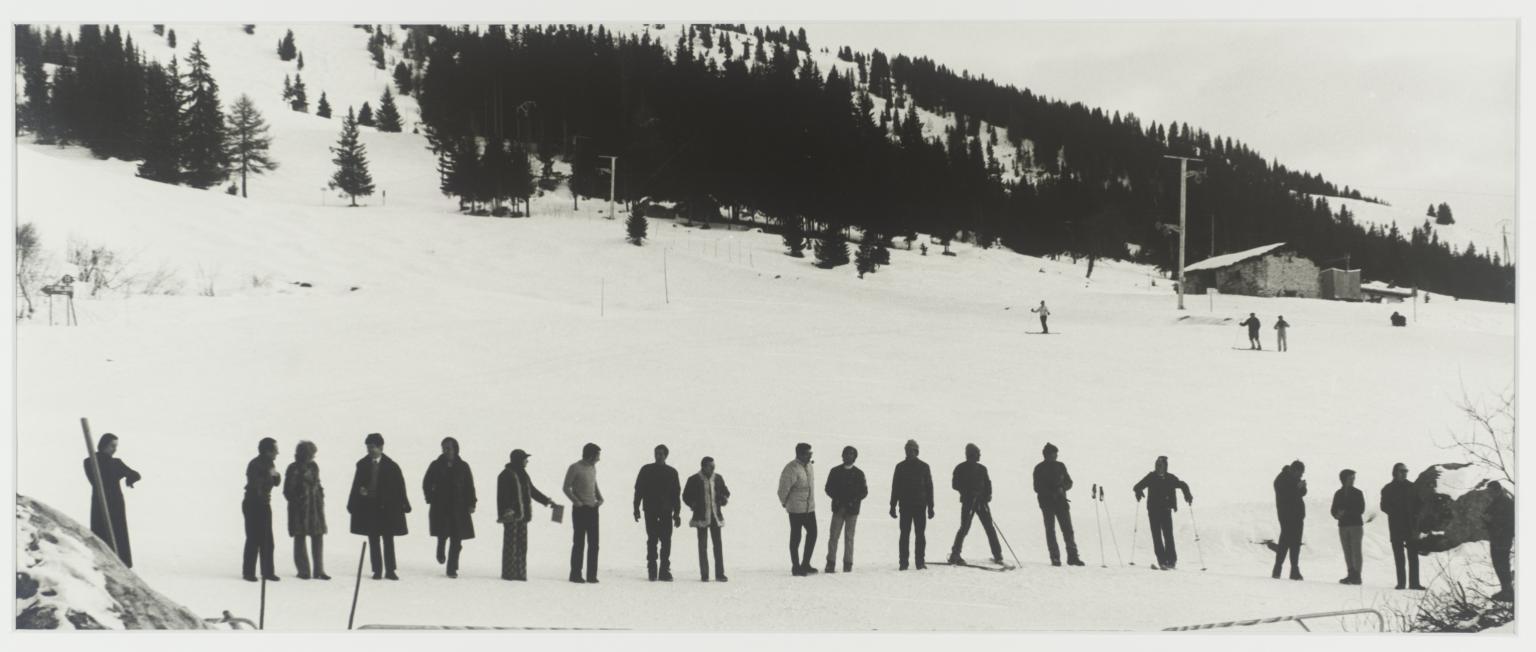

David Lamelas, Time 1970
This photograph documents the first presentation of Time, a performance conceived by David Lamelas, in Les Arcs in the French Alps. The performance begins when the first participant tells the time to the person next to them. They ‘receive’ the time and ‘hold on to it’ before sharing it with the following person. The process continues until the last person is reached, who then announces the time ‘to the world’ in a language of their choice. Lamelas says: ‘We may come from different cultures, be of different color or religion, but we all share the one single time of the present.’
Gallery label, January 2025
12/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
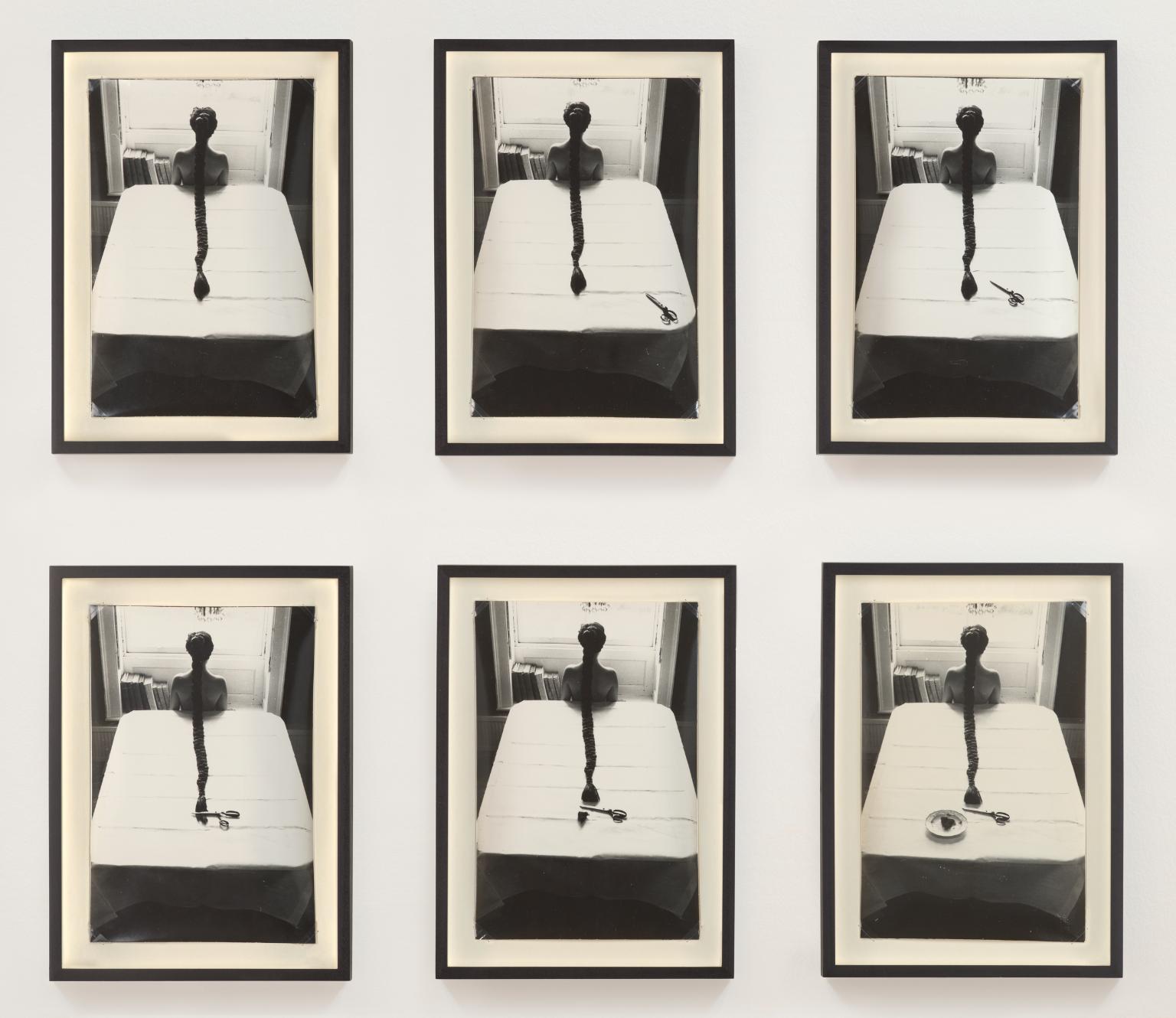

Rose English, Harriet and Plait 1976
Harriet and Plait depicts the artist’s sister Harriet sitting in front of a window and wearing a long, plaited wig. The sequence of photographs captures the tip of her plait being snipped off and placed on a plate, resembling a triangle of pubic hair. Rose English took the photographs in the dining room of her mother’s house in Herefordshire. English strove to challenge traditional categories in art in her practice, moving from working with objects to events. In the early 1970s, she began to incorporate hand-made items – such as this wig – in staged settings that she would later photograph.
Gallery label, January 2025
13/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
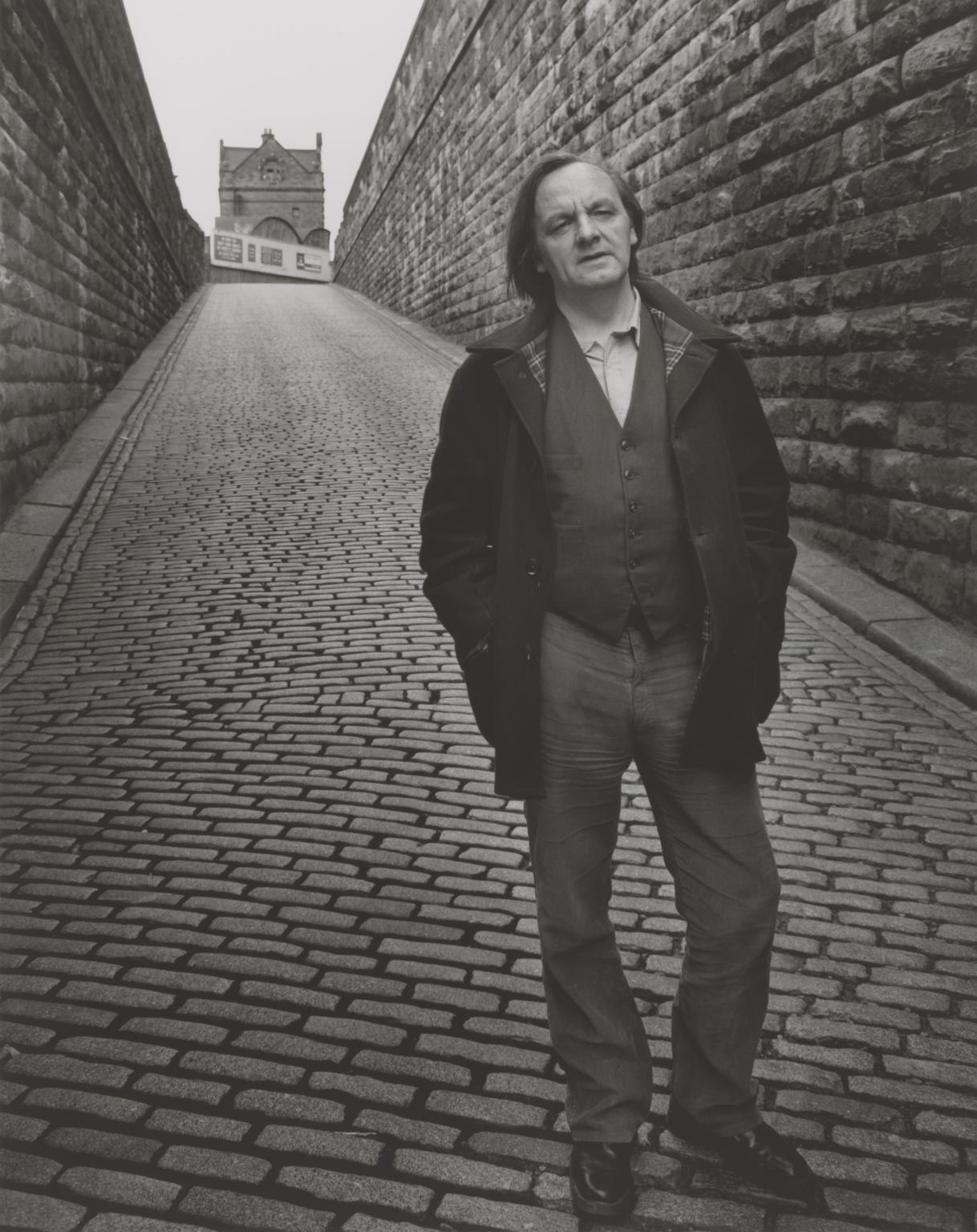

Chris Killip, Trade Union Official, Scottswood, Tyneside 1979, printed 2012–13
This group of images capture the changing landscapes of the northeast of England during a period of high unemployment and deindustrialisation. In these photographs, Chris Killip documents the windowless purpose-built homes that became typical across the northeast, the dying local shipbuilding industry, as well as community leaders such as a trade union official. Killip took these photographs after being made the Northern Arts Photography Fellow in Newcastle in 1975.
Gallery label, January 2025
14/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
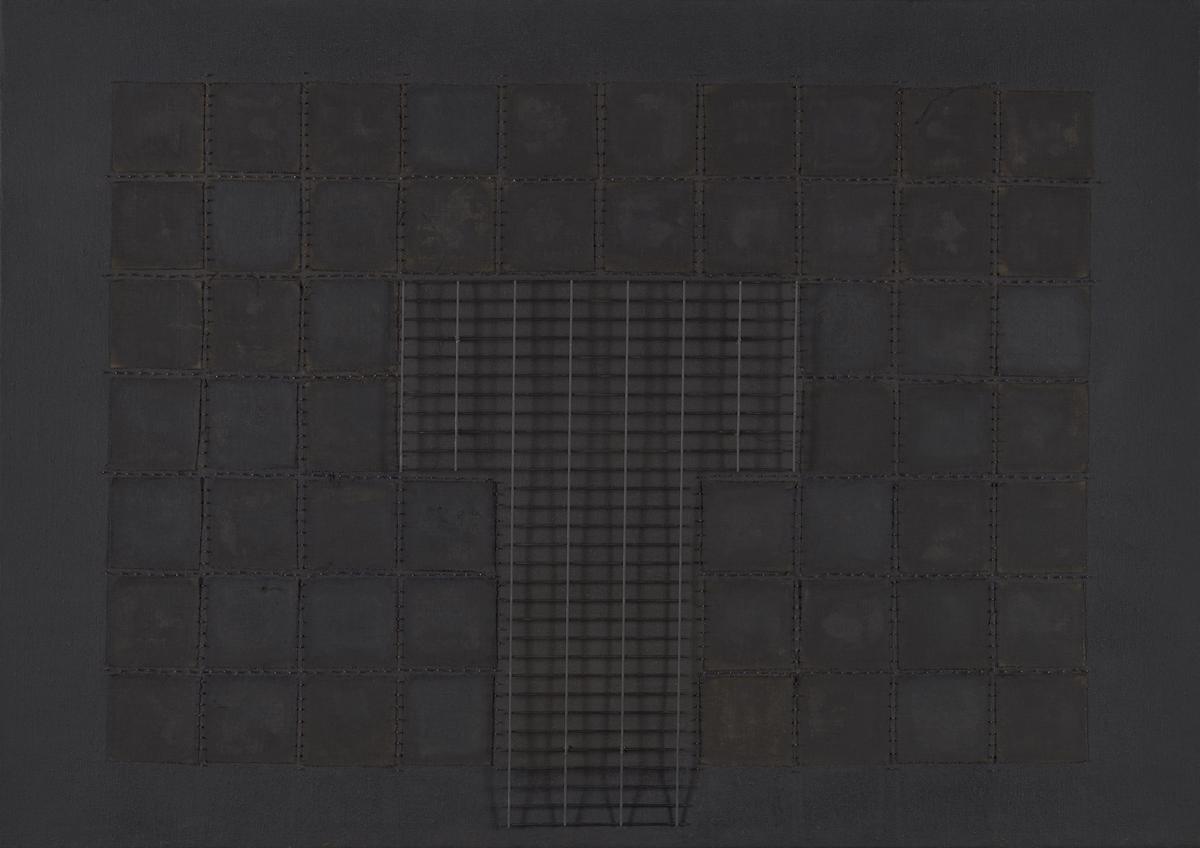
Donald Locke, Dageraad From the Air 1978–9
Dageraad was a sugar plantation. In 1763 it was the site of Guyana’s first rebellion of enslaved people. The painting evokes the plantation system that shaped Guyana’s history under Dutch and British colonial rule. The grid reflects the intervention on the land, sectioned by dykes and drainage canals. Donald Locke said: ‘In the Caribbean, the most dominant sociological event is the plantation system. I grew up at a time when the plantation system was still in existence. It dominated the sky; it dominated your life from beginning to end.’
Gallery label, September 2023
15/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
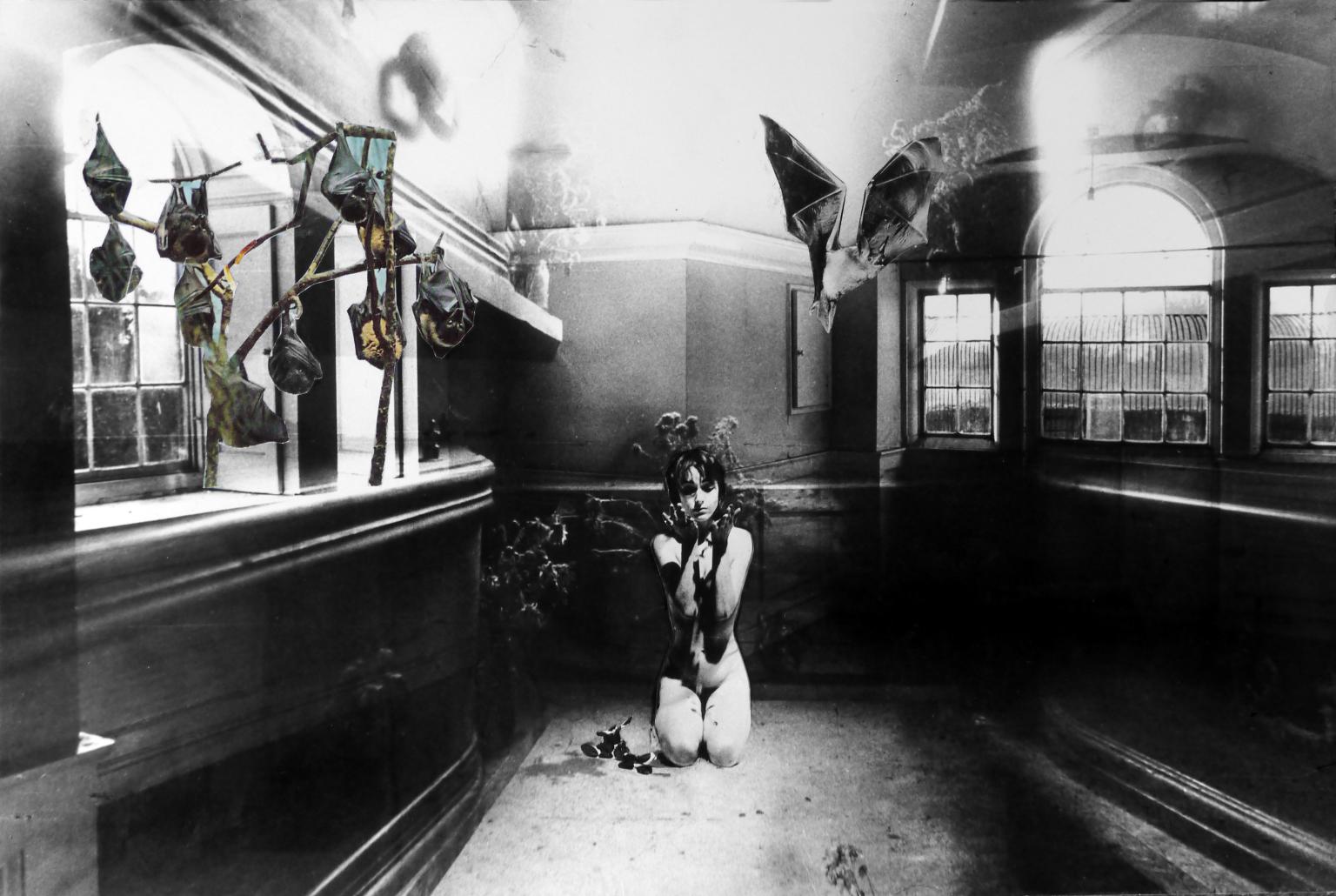

Penny Slinger, Dust to Dust 1970–7
These photo-collages are part of a series of self-portraits Penny Slinger made in the near derelict Lilford Hall in Northamptonshire. Speaking of the photographs, Slinger found: ‘They had an evocative power, which compelled me to use them as the basis for a series of collages. I felt that this Stately Home had something yet to contribute to my own exploration of the psyche.’ During the seven-year process of making the series, Slinger found herself ‘emerging from a nightmare of others’ projections.’ Her photo-collages were published in 1977 as a book titled An Exorcism.
Gallery label, January 2025
16/27
artworks in Ideas into Action

Richard Long CBE, Turf Circle 1966
Richard Long leaves the studio to create work in outdoor settings. During walks he subtly marks his presence. In the works represented here, he records a temporary impression on turf and picks daisies along two lines to form an ‘X’. These interventions won’t last, but are made permanent in the form of photographs. ‘These works are of the place, they are a rearrangement of it and in time will be reabsorbed by it. I hope to make work for the land, not against it,’ he said.
Gallery label, September 2023
17/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
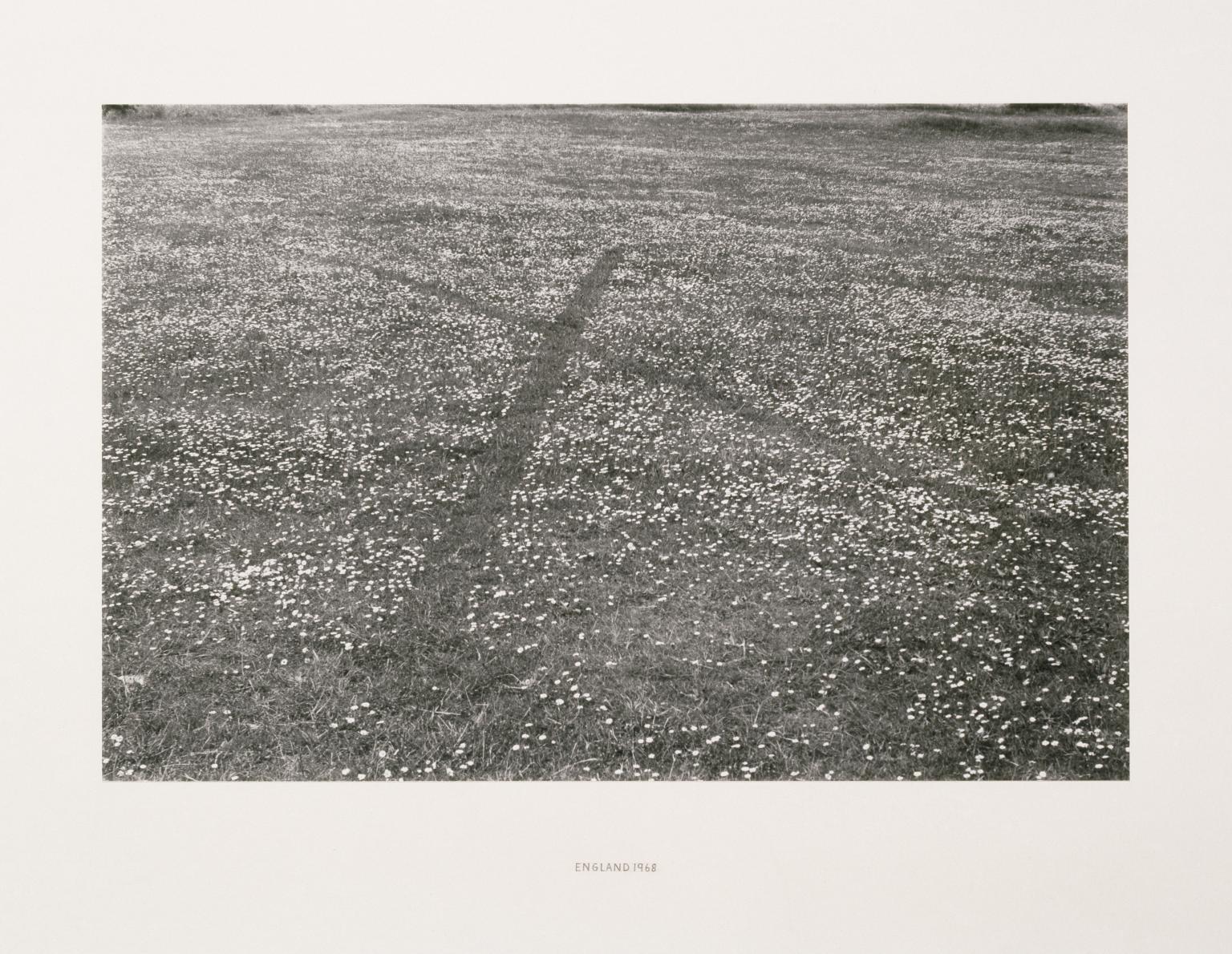

Richard Long CBE, England 1968 1968
Richard Long leaves the studio to create work in outdoor settings. During walks he subtly marks his presence. In the works represented here, he records a temporary impression on turf and picks daisies along two lines to form an ‘X’. These interventions won’t last, but are made permanent in the form of photographs. ‘These works are of the place, they are a rearrangement of it and in time will be reabsorbed by it. I hope to make work for the land, not against it,’ he said.
Gallery label, September 2023
18/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
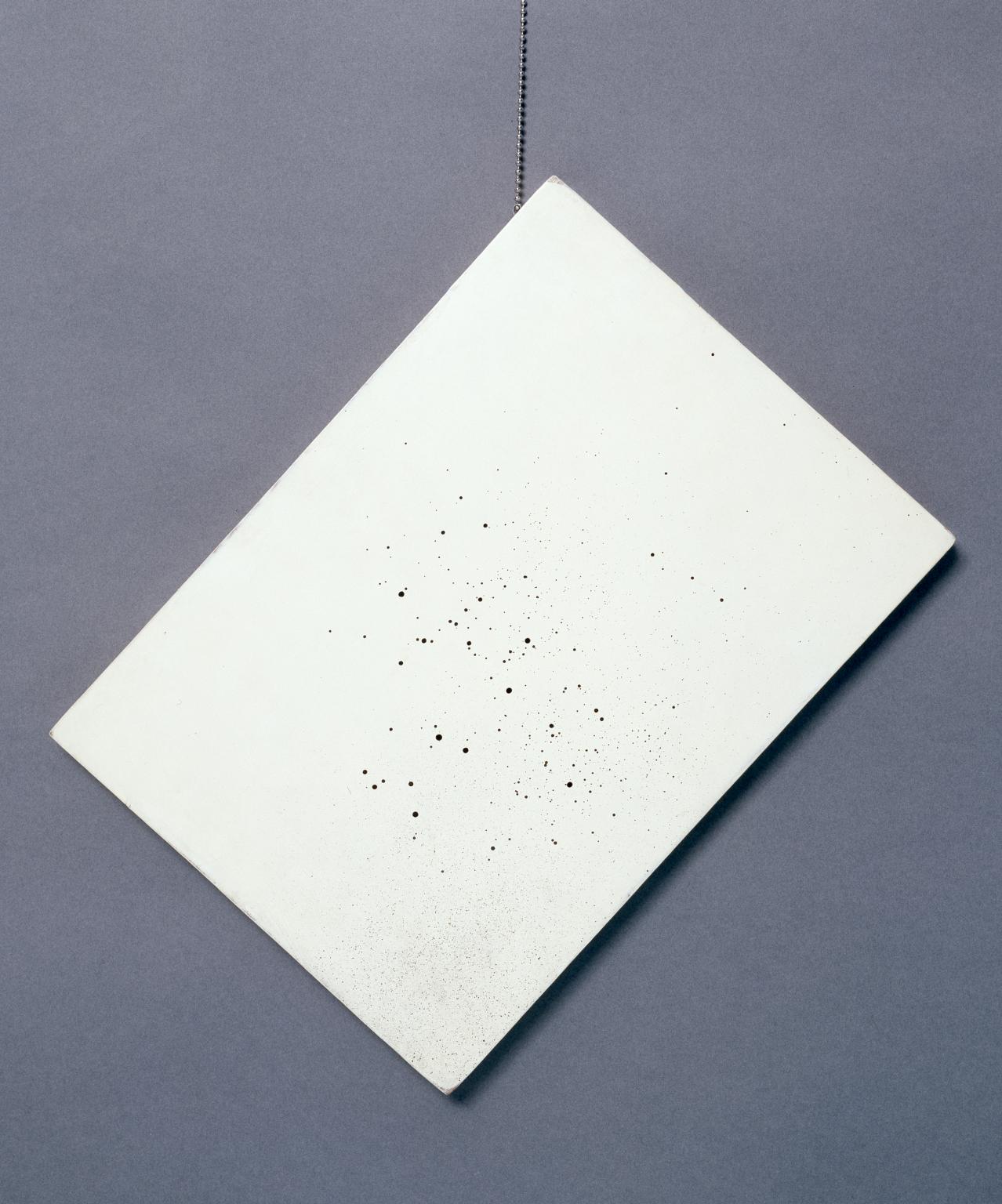

John Latham, One-Second Drawing (17” 2002) (Time Signature 5:1) 1972
This work comprises a wooden board painted white and covered with black flecks of paint. It is a part of a series of ‘One Second Drawings’ which John Latham began in 1970, each produced by spraying black paint onto a white board for one second. Through this simple act, Lathan aimed to represent his concept of a ‘least event’, which is the shortest departure from a state of nothingness. The numerical sequence in the title (17” 2002) records the time the work was executed: the 17th second of the 20th minute of the second hour.
Gallery label, January 2025
19/27
artworks in Ideas into Action

Mary Kelly, Post-Partum Document. Documentation III: Analysed Markings And Diary Perspective Schema (Experimentum Mentis III: Weaning from the Dyad) 1975
Chalk and crayon drawings by Mary Kelly’s son are overlayed with transcriptions, annotations and reflections based on their interactions as he began nursery. These panels are the third group of a six-part series, each documenting a formative moment in Kelly’s son's early life. Kelly has stated that Post-Partum Document is not ‘autobiographical’. She instead uses her story to suggest ‘an interplay of voices – the mother’s experience, feminist analysis, academic discussion, political debate’. The work subverts romanticised depictions of the mother-child relationship, presenting the experience as inevitably bound up with societal norms and gendered expectations.
Gallery label, January 2025
20/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
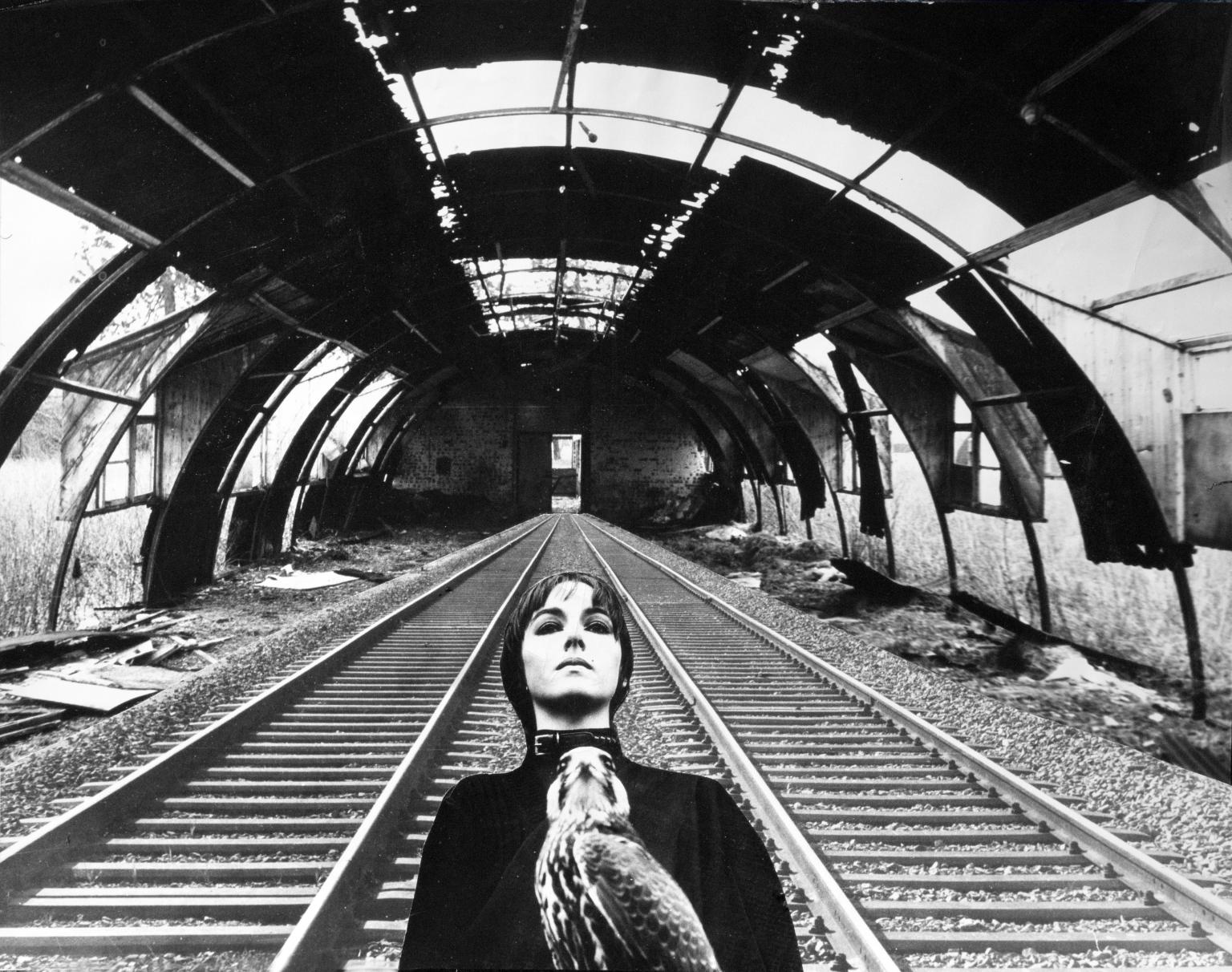

Penny Slinger, End of the Line 2 1977
These photo-collages are part of a series of self-portraits Penny Slinger made in the near derelict Lilford Hall in Northamptonshire. Speaking of the photographs, Slinger found: ‘They had an evocative power, which compelled me to use them as the basis for a series of collages. I felt that this Stately Home had something yet to contribute to my own exploration of the psyche.’ During the seven-year process of making the series, Slinger found herself ‘emerging from a nightmare of others’ projections.’ Her photo-collages were published in 1977 as a book titled An Exorcism.
Gallery label, January 2025
21/27
artworks in Ideas into Action

Sir Don McCullin CBE, A Jubilant Catholic Youth After Stoning British Soldiers, The Bogside, Londonderry, Northern Ireland 1971, printed 2013
22/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
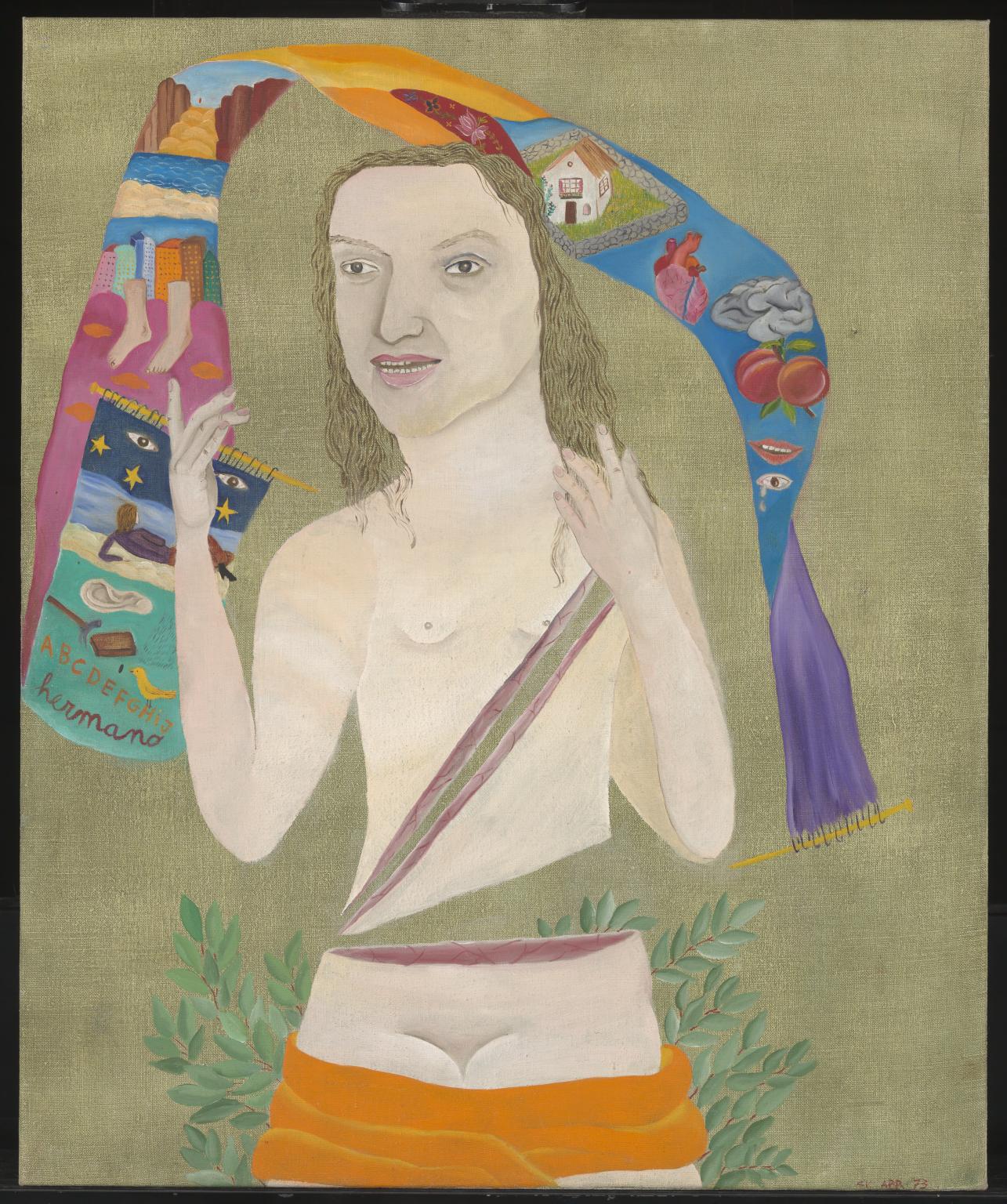

Cecilia Vicuña, Violeta Parra 1973
This painting is part of a series called Heroes of the Revolution. In 1952, singer and folklorist Violeta Parra embarked on a tour around rural Chile, recording and compiling folk music. She rescued a tradition that most Chileans had forgotten. This led to an artistic movement known as Nueva Canción Chilena (New Chilean Song). The painting commemorates Parra’s work and struggle before she took her own life in 1967. ‘My paintings are political in a personal way’, Vicuña has explained. ‘My canvases are born as representations of a socialist paradise where everything is possible’.
Gallery label, September 2023
23/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
Sir Horace Ové CBE, Barbara Beese at the Mangrove Demonstration 1970, printed 2023
On 9 August 1970, a march took place to protest the police harassment of Black communities, including at The Mangrove, a Caribbean restaurant in Notting Hill, London. Nine protesters were charged with incitement to riot. In these photographs, Horace Ové captures significant moments from the march and subsequent trial. All nine activists were eventually acquitted, signalling the first judicial acknowledgment of racial hatred within the Metropolitan Police. These photographs come from a body of work Ové made between 1967 and 1970 documenting key events in the British civil rights movement.
Gallery label, August 2024
24/27
artworks in Ideas into Action

Romany Eveleigh, Pages 1976
Romany Eveleigh covered a sheet of paper with a layer of black ink, followed by a layer of white oil paint. Scratching hundreds of small circles into the wet paint, she revealed the dark ink beneath. The resulting pattern, which can be read as repetitions of the letter ‘o’, is reminiscent of text. The formation of the circles into columns suggests the pages of a book, with blocks of text and empty margins. Eveleigh’s use of the visual language of writing and printing was inspired by the tabloid newsprint pages plastered on walls in the streets of Rome where she lived.
Gallery label, January 2025
25/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
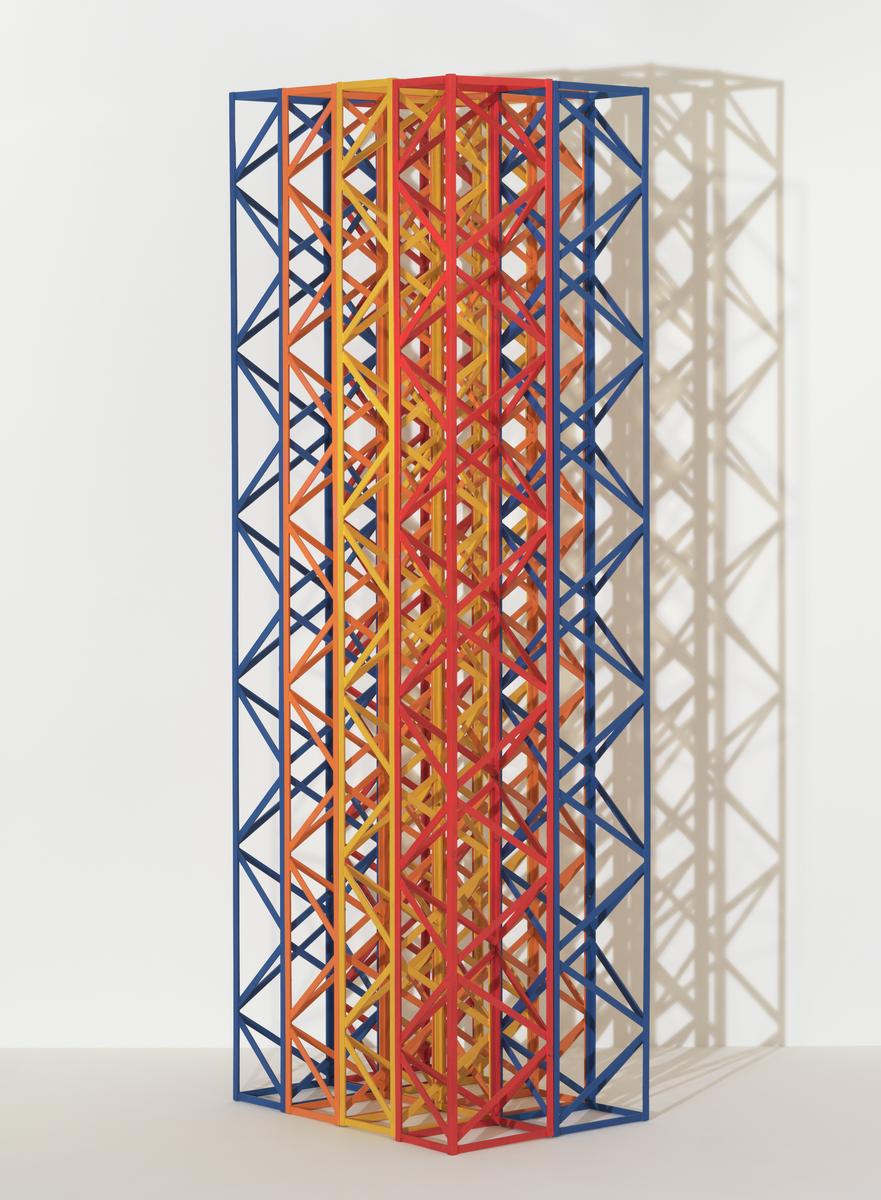
Rasheed Araeen, Rang Baranga 1969
Rang Baranga is made from an intersecting lattice structure composed of eight individual columns, each painted in a sequence of contrasting colours. The title is an Urdu term meaning ‘of many colours’. Trained as a civil engineer in Karachi, Pakistan, Rasheed Araeen creates sculptures that reference architectural and engineering structures as well as modernist art. In his search for stable yet open configurations, he found inspiration in nature, particularly in the movement of fire and water. Araeen was also struck by the sculptural language of Anthony Caro (displayed in this room), whose work he encountered after moving to London in 1964.
Gallery label, August 2024
26/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
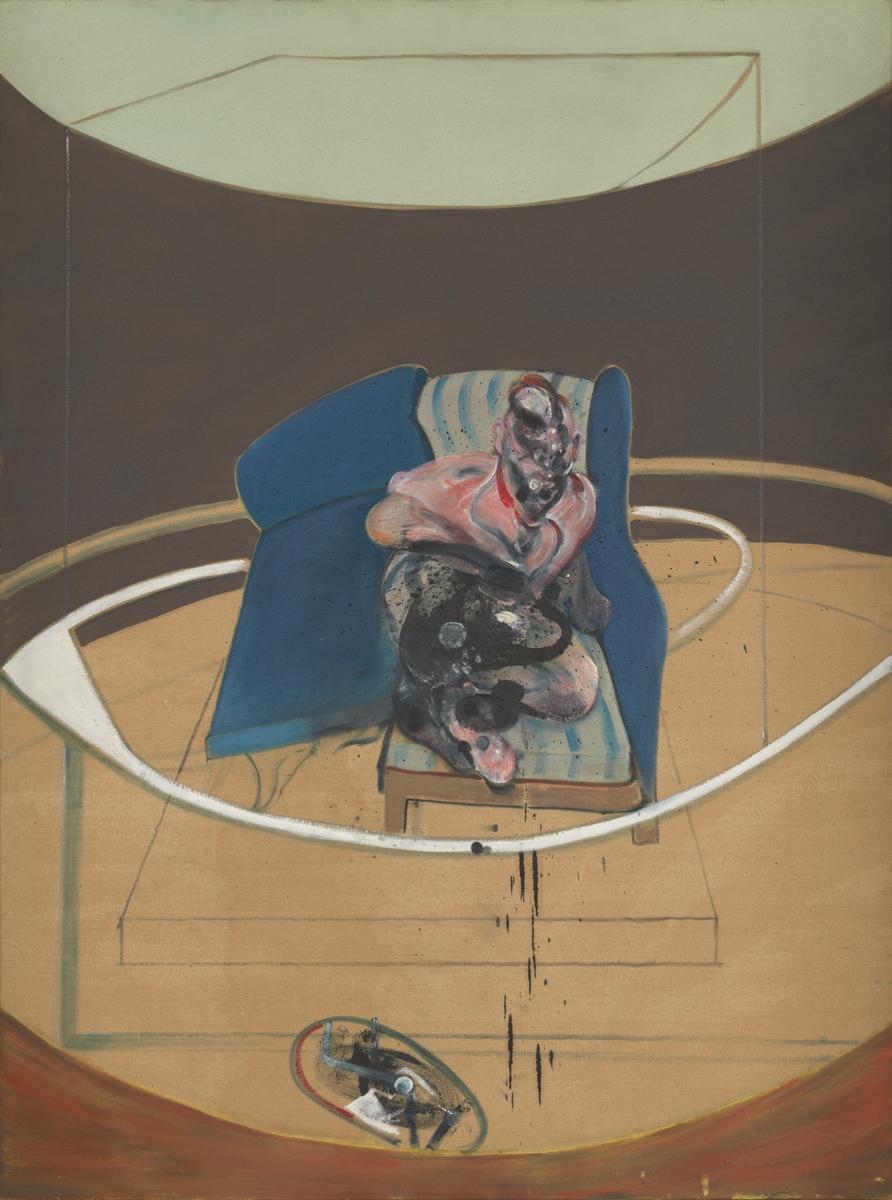

Francis Bacon, Study for Portrait on Folding Bed 1963
A partially clothed male figure, wearing a rolled sleeved shirt, lies on an unmade folding bed. The head and lower body are rendered with distortion and ambiguity, with the texture and visceral colours evoking the flesh, bone and blood. The dribbles and splatters of paint give the appearance of leaking bodily fluids. Francis Bacon found the image disappointing, regretting the oval at the bottom and the absence of the carpet, remarking ‘I wish they (Tate) would burn it.’
Gallery label, October 2025
27/27
artworks in Ideas into Action
Art in this room






Sorry, no image available



Sorry, no image available












Sorry, no image available



You've viewed 6/27 artworks
You've viewed 27/27 artworks
